The Caribbean Island of Dominican Republic
|

The Dominican Republic is a nation on the island of Hispaniola, part of the Greater Antilles
archipelago in the Caribbean region. The western third of the island is occupied by the nation of
Haiti, making Hispaniola one of two Caribbean islands that are occupied by two countries, Saint
Martin being the other. Both by area and population, the Dominican Republic is the second largest
Caribbean nation (after Cuba), with 48,442 km² and an estimated 10. million people.
Inhabited by Taínos since the 7th century, the Dominican Republic was reached by Christopher
Columbus in 1492 and became the site of the first permanent European settlement in the Americas,
namely Santo Domingo, the country's capital and Spain's first capital in the New World. In Santo
Domingo stand, among other firsts in the Americas, the first university, cathedral, and castle, the
latter two in the Ciudad Colonial area, a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
After three centuries of Spanish rule, with French and Haitian interludes, the country became
independent in 1821 but was quickly taken over by Haiti. It attained independence in 1844, but
mostly suffered political turmoil and tyranny, and as well a brief return to Spanish rule, over the
next 72 years. United States occupation 1916-24 and a subsequent, calm 6–year period were followed
by the military dictatorship of Rafael Leonidas Trujillo Molina to 1961. The last civil war, in
1965, ended with U.S. intervention, followed by the authoritarian rule of Joaquin Balaguer, to
1978. Since 1978, the Dominican Republic has moved strongly toward representative democracy.
|
|

History - The Taínos
The inhabitants of Hispaniola were displaced by the Taínos, an Arawakan-speaking people, circa A.D.
600. The Taínos called the island Kiskeya or Quisqueya, meaning "mother of the earth", as well as
Haití or Aytí, and Bohio. They engaged in farming and fishing, and hunting and gathering. For much
of the 15th century, the Taíno tribe was being driven to the Northeast in the Caribbean (out of
what is now South America) because of raids by fierce Caribs. There are widely varying estimates of
the population of Hispaniola in 1492, including one hundred thousand, three hundred thousand, and
four hundred thousand to two million. By 1492 the island was divided into five chiefdoms.
Within a few years following the arrival of Europeans the population of Taínos had declined
drastically, due to changes in lifestyle, smallpox and other diseases that arrived with the
Europeans, intermarriage, and enslavement. By 1711 the Taíno numbered just 21,000. The last record
of pure Taíno natives in the country was from an 1864 account by a Spanish soldier during the
Restoration War, who wrote of Taínos shooting at Spanish soldiers and fleeing. Taíno cave paintings
can still be seen in a variety of caves around the country. Remnants of the Taino culture still
live on. Their designs of ancient pottery are still used today by skilled ceramic artisans in the
small artisan village of Higüerito, Moca.
|
|

Independence
In 1838 Juan Pablo Duarte founded a secret society called La Trinitaria, which sought the
complete independence of Santo Domingo without any foreign intervention. Ramón Matías Mella and
Francisco del Rosario Sánchez (the latter of partly African ancestry), despite not being among the
founding members of La Trinitaria, were decisive in the fight for independence.
Duarte and they are the three Founding Fathers of the Dominican Republic. On February 27, 1844,
the Trinitarios (Trinitarians), declared the independence from Haiti. They were backed by Pedro
Santana, a wealthy cattle rancher from El Seibo, who became general of the army of the nascent
Republic. The Dominican Republic's first Constitution was adopted on November 6, 1844, and was
modeled after the United States Constitution.
The decades that followed were filled with tyranny, factionalism, economic difficulties, rapid
changes of government, and exile for political opponents. Threatening the nation's independence
were renewed Haitian invasions occurring in 1844, 1845-49, 1849-55, and 1855-56.
Meanwhile, archrivals Santana and Buenaventura Báez held power most of the time, both ruling
arbitrarily. They promoted competing plans to annex the new nation to another power: Santana
favored Spain, and Báez the United States.
|
Geography
|
|
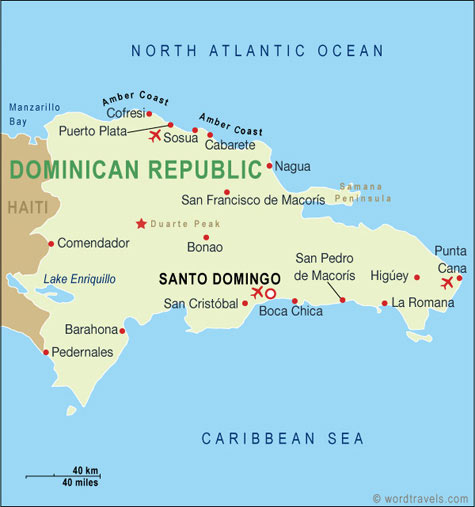
The Dominican Republic is situated on the eastern part of the second-largest island in the
Greater Antilles, Hispaniola. It shares the island roughly at a 2:1 ratio with Haiti. The whole
country measures an area of 48,442 km² (or 48,730 km², or 48,921 km²) making it the second largest
country in the Antilles, after Cuba. The country's capital and greatest metropolitan area, Santo
Domingo, is located on the southern coast.
There are many small offshore islands and cays that are part of the Dominican territory. The two
largest islands near shore are Saona, in the southeast, and Beata, in the southwest. To the north,
at distances of 100–200 kilometres (62–120 mi), are three extensive, largely submerged banks, which
geographically are a southeast continuation of the Bahamas: Navidad Bank, Silver Bank, and Mouchoir
Bank. Navidad Bank and Silver Bank have been officially claimed by the Dominican Republic.
The country's mainland has four important mountain ranges. The most northerly is the Cordillera
Septentrional ("Northern Mountain Range"), which extends from the northwestern coastal town of
Monte Cristi, near the Haitian border, to the Samaná Peninsula in the east, running parallel to the
Atlantic coast. The highest range in the Dominican Republic — indeed, in the whole of the West
Indies — is the Cordillera Central ("Central Mountain Range"). It gradually bends southwards and
finishes near the town of Azua, on the Caribbean coast. In the Cordillera Central are found the
four highest peaks in the Caribbean: Pico Duarte (3,098 metres/10,160 feet above sea level), La
Pelona (3,094 metres/10,150 feet, La Rucilla (3,049 metres/10,000 feet) and Pico Yaque
South shore of Lake Enriquillo, looking northward to the Sierra de Neiba.
Four major rivers drain the numerous mountains of the Dominican Republic. The Yaque del Norte is
the longest and most important Dominican river. It carries excess water down from the Cibao Valley
and empties into Monte Cristi Bay, in the northwest. Likewise, the Yuna River serves the Vega Real
and empties into Samaná Bay, in the northeast. Drainage of the San Juan Valley is provided by the
San Juan River, tributary of the Yaque del Sur, which empties into the Caribbean, in the south. The
Artibonito is the longest river of Hispaniola and flows westward into Haiti.
There are many lakes and coastal lagoons. The largest lake is Enriquillo, a salt lake at 40
metres (130 ft) below sea level, the lowest point in the Caribbean. Other important lakes are
Laguna de Rincón or Cabral, with freshwater, and Laguna de Oviedo, a lagoon with brackish
water.
|
Economy
|
|
Symbols and name
Some of the important symbols include the flag, the coat of arms, and the national anthem,
titled Himno Nacional. The flag has a large white cross that divides it into four quarters. Two
quarters are red and two are blue. Red represents the blood shed by the liberators. Blue expresses
God's protection over the nation. The white cross symbolizes the struggle of the liberators to
bequeath future generations a free nation. An alternate interpretation is that blue represents the
ideals of progress and liberty, whereas white symbolizes peace and unity amongst Dominicans. In the
center of the cross is the Dominican coat of arms, in the same colors as the national flag.
The national flower is that of the West Indian Mahogany (Swietenia mahagoni). The national bird
is the Cigua Palmera or Palmchat (Dulus dominicus).
For most of its history (up to independence) the colony was known by the name of its present
capital, Santo Domingo. At present, the Dominican Republic is one of the few countries in the world
with a demonym–based name (as the Czech Republic, et al.). For example, the French Republic is
generally known as France, but the Dominican Republic has no such equivalent – although the name
"Quisqueya" is used sometimes.
The Dominican Republic has the largest or second largest economy in Central America and the
Caribbean. It is a lower middle-income developing country, with a 2007 GDP per capita of $9,208, in
PPP terms, which is relatively high in Latin America. In the trimester of January–March 2007 it
experienced an exceptional growth of 9.1% in its GDP, which was actually below the previous year's
10.9% in the same period. Growth was led by imports, followed by exports, with finance and foreign
investment the next largest factors.
The D.R. is primarily dependent on natural resources and government services.
Although the service sector has recently overtaken agriculture as the leading employer of
Dominicans (due principally to growth in tourism and Free Trade Zones), agriculture remains the
most important sector in terms of domestic consumption and is in second place, behind mining, in
terms of export earnings. The service sector in general has experienced growth in recent years, as
has construction. Free Trade Zone earnings and tourism are the fastest-growing export sectors. Real
estate tourism alone accounted for $1.5 billion in earnings for 2007. Remittances from Dominicans
living abroad amounted to nearly $3.2 billion in 2007.
Currency
The Dominican peso (DOP, or RD$) is the national currency, although United States dollars (USD) and
euros (EUR) are also accepted at most tourist sites. The U.S. dollar is implicated in almost all
commercial transactions of the Dominican Republic; such dollarization is common in high inflation
economies. The peso was worth the same as the USD until the 1980s, but has depreciated. The
exchange rate in 1993 was 14.00 pesos per USD and 16.00 pesos in 2000, but it jumped to 53.00 pesos
per USD in 2003. In 2004, the exchange rate was back down to around 31.00 pesos per USD. As of
February 2009 the exchange rate was 1 DOP = 0.0281 USD, i.e. 35.65 DOP per USD; 1 DOP = 0.022 euros
(EUR, or €); and 1 DOP = 2.74 Japanese yen (JPY, or ¥).
Tourism
Tourism is fueling the Dominican Republic's economic growth. For example, the contribution of
travel and tourism to employment is expected to rise from 550,000 jobs in 2008 — 14.4% of total
employment or 1 in every 7 jobs — to 743,000 jobs — 14.2% of total employment or 1 in every 7.1
jobs by 2018. With the construction of projects like Cap Cana, San Souci Port in Santo Domingo, and
Moon Palace Resort in Punta Cana, the Dominican Republic expects increased tourism activity in the
upcoming year. Ecotourism has been a topic increasingly important in the nation, with towns like
Jarabacoa and neighboring Constanza, and locations like the Pico Duarte, Bahia de Las Aguilas and
others becoming more significant in attempts to increase direct benefits from tourism.
Population
The population of the
Dominican Republic in 2007 was estimated by the United Nations at 9,760,000, which placed it number
82 in population among the 193 nations of the world. In that year approximately 5% of the
population was over 65 years of age, while 35% of the population was under 15 years of age. There
were 103 males for every 100 females in the country in 2007. According to the UN, the annual
population growth rate for 2006–2007 is 1.5%, with the projected population for the year 2015 at
10,121,000.
It was estimated by the Dominican government that the population density in 2007 was 192 per km²
(498 per sq mi), and 63% of the population lived in urban areas.
The southern coastal plains and the Cibao Valley are the most densely populated areas of the
country. The capital city, Santo Domingo, had a population of 3,014,000 in 2007. Other important
cities are Santiago de los Caballeros (pop. 756,098), La Romana (pop. 250,000), San Pedro de
Macorís, San Francisco de Macorís, Puerto Plata, and La Vega. Per the United Nations, the urban
population growth rate for 2000–2005 was 2.3%.
|
What to wear in Dominican Republic
|
|
Weather is one of the main factors that will play
a part in what kind of clothing travelers will want to bring on their trip to the Dominican
Republic. The climate on the island is generally warm with little variation. There is some heavy
rainfall during certain times of year on the island so vacationers should pack some rain gear in
case of rain showers.
Social setting is also important when considering what clothing items to pack. Religion is
important to the every day lives of the Dominicans, who are mostly Roman Catholic. If you plan on
visiting a church, or attending a religious ceremony tourists should remember that the style of
dress is usually conservative.
Do not wear shorts to church, and it is respectful for women to cover their heads before
entering the church building. Also, men should remove hats or any head coverings before entering
the church as a sign of respect. Local women often wear long sleeves and veils when attending
church services.
Most resorts are fairly informal when it comes to appropriate attire. Shorts and bathing suits
under a wrap, are considered acceptable most of the time at breakfast and lunch. Dinner time is
usually more formal, and long pants and skirts, and collared shirts are normally worn. Restaurants
in certain places, like Santo Domingo, sometimes have a stricter dress code. At lunch and dinner,
it is suggested that men wear trousers and women wear dresses.
Dominican people dress similarly to Americans. Most wear summer clothes, like sandals, T-shirts,
skirt, light jackets and sweaters. For special occasions, women may wear long dresses and skirts in
bright colors like orange and yellow. Spanish influence is also present in the way that people in
The Dominican Republic dress. Article source: http://dominicanrepublic-guide.info
|
Dominican Republic Marriage Requirements
|
The information below outlines the marriage requirements for getting married in Dominican
Republic
# No waiting period
# No blood test
# Two witnesses required
# US citizens are required to write to the American Consulate in Santo.Domingo requesting
permission to marry
* Parties must be at least 18 years of age to marry
Documents required
* Passport,
* original birth certificate,
* single status affidavit in Spanish for each party, joint affidavits not
acceptable. These must be notarized and state wether the bride or groom has ever been married,
divorced, or widowed.
* divorce decree or death certificate for partner in Spanish.
* According to Dominican Law a divorced woman has to wait 10 months before
remarrying unless she is marrying the same man she divorced or she was divorced under special DR
law. Then the ruling is a waiting period of 24 hours.
Fees
US$60 - $100 depending upon judge.
(Spanish documents can be prepared by the Dominican consulate nearest your residence.)
Most hotels have wedding coordinators on site to help you, however, be warned, they like to
receive paperwork at least 15 days in advance to prepare for your wedding.
You will be given a document that proves the wedding took place after the ceremony. You then
need to request a marriage certificate from the local Justice of the Peace. The document issued by
the Justice of the Peace is a valid marriage certificate anywhere in the world.
Registrars Offices
The registrar's office should be contacted for specific rules regarding planning your
destination or beach wedding in Dominican Republic. They will also provide information regarding
marriage licenses and marriage certificates.
http://www.islandbrides.com
|
Dominican Republic things to do
|
|

Ocean World Dolphin
Swim
Find out why the dolphin swim is the most popular program at Ocean
World! During your 30-minute encounter you'll dance, hug, pet and swim with the dolphins.
Finishing
Mike's Marina Fishing Charters is the
longest running professional Sportfishing Outfitter in Punta Cana, operating from a real Marina
with full Marina's Dock Services, Fuel Station,Immigrations and Customs Services on the same
property. All sportfishing Yachts are Top vessels equipped with Top Brand Sportfishing gear like
Penn Intls, Shimano TLD's, Shimano Tiagra's, running offshore Billfishing, offshore deep Bottom
Fishing, Catamaran Cruises, offshore Yacht Cruises, FamilySnorkelYachtCruises and everything
related to watersports activities.
The park area at the shores of Lago
Enriquillo are unattended on some days. No visitors or park personel can feel strange, but it
is not Europe. The lizards are there however, scrambling in the sand,
Dominican Republic Monster Truck
Safari
Heads and shoulders above the rest -- join a unique tour of the
Dominican Republic on an 8x8 Monster Truck Safari! Go where the tour buses cannot as you enter the
depths of the island exploring the unspoiled Dominican countryside. Traveling by 8x8 monster truck
allows you to see breathtaking landscape while traveling along back country roads, crossing rivers,
streams and sugar cane fields. Visit small colorful villages and see how the local people live,
their typical homes and a school. For the coffee connoisseur, take some time to taste the locally
brewed Dominican Coffee, one of the country's most famous products.
Tropical Storm Bavaro Cruise
Board the Tropical Storm to enjoy a slow and relaxing sail from Punta Cana, over the crystal clear
aqua waters of the Caribbean, along the stunning, white sandy coastline of Bavaro. Start your day
with a visit to the wreck of the Astron, a sunken freighter which lies in shallow water close
to the shore. Here you can see large schools of blue fish, barracuda and yellowtail snapper.
Caribbean Festival Snorkel Cruise
Come on board for an unforgettable day of cruising, snorkeling and dancing. Sit back and relax as
you cruise along the stunning Bavaro coastline. Add a little adventure to your day and snorkel in
the crystal clear waters. Enjoy a Caribbean dance show and join in the dancing for an experience
not to be missed. You will stop at a popular snorkeling site, known for regular sightings of sharks
and rays. Slip into the water for a guided snorkeling tour through the warm waters, giving you an
introduction to the colorful marine life of the Caribbean.
Bay of Sosua Catamaran Cruise and
Snorkeling
Be a millionaire for a day as you sail on a 54ft catamaran along
the North Coast from the Bay of Playa Dorada to the beautiful bay of Sosua. Let the wind carry you
to magnificent hidden beaches bordered by crystal clear waters and enjoy the wild, intact beauty of
the Dominican Republic's fine sand beaches.
The crew are available to assist you with snorkeling tuition if required (equipment available
onboard), before you plunge into the clear blue waters which teem with tropical fish. Explore the
beautiful reefs and varied marine life before returning to the boat for a buffet lunch onboard -
drinks included!
|
|